EPC Develops 6 kW 800 VDC GaN Converter for Next-Generation AI Data Centres
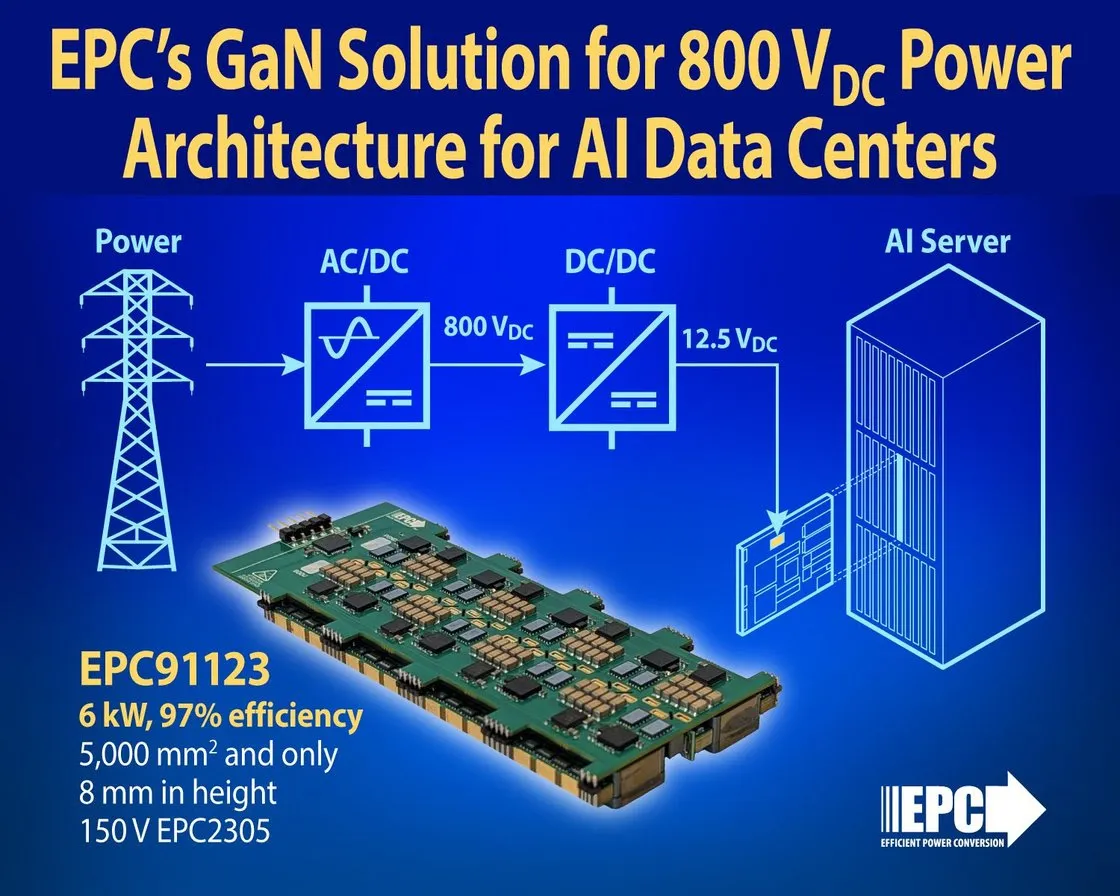 As AI data centres evolve toward megawatt-scale power systems, designers are being forced to rethink the way energy is delivered to the rack. Traditional 54 V and 400 V architectures are reaching their limits, and losses between conversion stages are becoming too large to ignore. To address this, Efficient Power Conversion (EPC) has developed a low-cost, low-profile 6 kW GaN-based converter that steps 800 VDC down to 12.5 VDC using an Input Series Output Parallel (ISOP) topology.
As AI data centres evolve toward megawatt-scale power systems, designers are being forced to rethink the way energy is delivered to the rack. Traditional 54 V and 400 V architectures are reaching their limits, and losses between conversion stages are becoming too large to ignore. To address this, Efficient Power Conversion (EPC) has developed a low-cost, low-profile 6 kW GaN-based converter that steps 800 VDC down to 12.5 VDC using an Input Series Output Parallel (ISOP) topology.
Rethinking Rack-Level Power Distribution
Today’s AI racks rely on multiple power stages: AC to 400 VDC, 400 VDC to 54 VDC, 54 VDC to 12 VDC, and finally 12 VDC to core voltage. Each stage adds cost, heat, and space overhead. EPC’s new approach simplifies this chain by distributing 800 VDC directly to the compute trays, where compact converters reduce it immediately to 12.5 V close to the load. This eliminates one full conversion step and dramatically cuts bussing losses across the rack.
The result is a system that is both simpler and more scalable. EPC’s converter occupies less than 5,000 mm² of board area, stands just 8 mm tall, and achieves over 97 percent efficiency, freeing valuable space for GPUs and cooling systems.
Inside the ISOP Topology
At the heart of the design is an ISOP configuration that divides the 800 V input and 12.5 V output among eight smaller converter modules. Each module handles only one-eighth of the total voltage and current, effectively transforming an 800 V-to-12.5 V challenge into an easier 100 V-to-12.5 V conversion.
Each submodule is built as an LLC resonant converter operating at 1 MHz, using EPC’s latest 150 V EPC2305 and 40 V EPC2366 eGaN FETs. The high-frequency switching allows the use of compact planar transformers, reducing the height and improving thermal management. The ISOP configuration also balances voltage and current automatically across modules, distributing losses evenly and simplifying cooling.
Efficiency Through GaN
EPC’s use of enhancement-mode GaN devices brings low resistance, low capacitance, and near-zero reverse recovery, which together make high-frequency operation practical at these voltage levels. The result is a converter that not only shrinks size but also increases overall system efficiency.
By integrating the conversion stage at the board level, EPC’s design reduces the need for large intermediate buses and heavy cabling, while improving transient response and load regulation close to the processors.
Towards the 800 V Ecosystem
EPC has developed this architecture in collaboration with NVIDIA, aligning it with the emerging 800 VDC infrastructure that many hyperscale operators are now exploring. The converter serves as a practical building block for future AI factories where each rack may draw tens of kilowatts from a common 800 VDC bus.
The modular approach also makes it inherently scalable. Additional ISOP modules can be paralleled to raise output power, enabling the same design principles to support multi-megawatt systems without major architectural changes.
Why It Matters
Moving from 400 V to 800 VDC power distribution is one of the most significant shifts in data-centre electrical design since the adoption of 48 V. EPC’s GaN-based solution shows how wide-bandgap devices can make this transition practical, reducing conversion stages, increasing power density, and improving the efficiency of next-generation AI infrastructure.
Learn more and read the original article on www.epc-co.com.




